Symptoms & Conditions
Symptoms of Tourette Syndrome
The early symptoms of Tourette syndrome are almost always noticed first in childhood, with the average between the ages of 7 and 10 years. Tourette syndrome occurs in people from all ethnic groups; males are affected about three to four times more often than females. Even though tourette syndrome can be a chronic condition with symptoms lasting a lifetime, most people with the condition experience their worst symptoms in their early teens, with improvement occurring in the late teens and continuing into adulthood.
The main symptoms of Tourette Syndrome are tics. Tics are sudden, repetitive, purposeless motor or vocal expressions or movements and can be classified under simple or complex.
Examples of Tics
The following video below shows some of the different types of tics shown by an individual with Tourette Syndrome from UK.
Classification of Tics
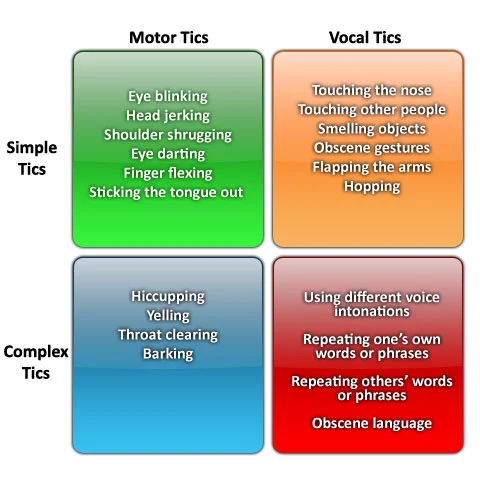
Tics Classification
Tics involve movement (motor tics) and sound (vocal tics). They’re classified in two ways:
- Simple tics, which are sudden, brief and repetitive and involve a limited number of muscle groups
- Complex tics, which are distinct, coordinated patterns of movements involving several muscle groups
Simple tics
Simple motor tics are sudden, brief, repetitive movements that involve a limited number of muscle groups. Some of the more common simple tics include eye blinking and other vision irregularities, facial grimacing, shoulder shrugging, and head or shoulder jerking. Simple vocalizations might include repetitive throat-clearing, sniffing, or grunting sounds.
Complex tics
Complex tics are distinct, coordinated patterns of movements involving several muscle groups. Complex motor tics might include facial grimacing combined with a head twist and a shoulder shrug. Other complex motor tics may actually appear purposeful, including sniffing or touching objects, hopping, jumping, bending, or twisting.
Vocal tics
Compulsive barking and grunting noises, have frequent throat clearing, coughing or sniffling, echolalia (vocal tics characterized by repeating words that a child hears), and/or coprolalia (vocal tics characterized by repeating or shouting obscene words), although coprolalia is rare.
Common motor tics
Eye blinking, jerking the head, movements of the eyes, different facial expressions, including grimacing, and nose twitching.
Coexisting Conditions
In addition to tics, children with Tourette syndrome are also likely to have emotional and behavior problems or comorbid conditions, have difficulty in school and poor self esteem and they are more likely to have symptoms of obsessive compulsive disorder, anxiety disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Different tics may develop over time. Tourette symptoms are most often at their worst during the teenage years and then sometimes get better during the transition to adulthood.
References:
2 Responses to "Symptoms & Conditions"
copic markers cheap…
[…]just below, are some totally unrelated sites to ours, however, they are definitely worth checking out[…]…
Leave a comment